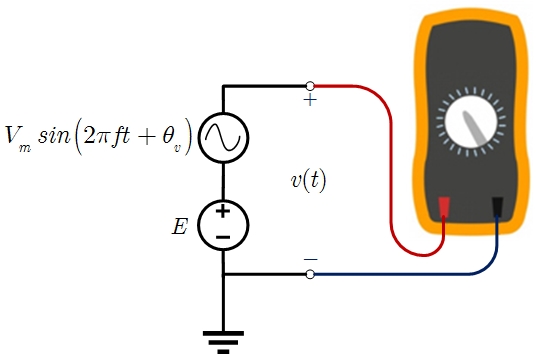
Set the variables to obtain \(v(t)=3+10sin(10\pi t+30^\circ ) \) and observe the characteristics of the waveform.
 0.000
0.000
Click on the toggle switch of the DMM to switch between DC and RMS readings.
Use the knobs to adjust the time per division and volts per division.